
Maintaining Back Health through Proper Lifting Techniques
Introduction
Proper lifting techniques are essential in preventing back injuries, a common issue in various occupational settings. Even lifting light objects incorrectly can lead to significant back strain. The use of back belts and adherence to recommended practices can mitigate these risks. This article examines the importance of proper lifting techniques and provides practical tips for maintaining back health, supported by guidelines from OSHA, NIOSH, and ACP.
The Role of Back Belts
Back belts are not a substitute for proper lifting techniques. They offer support for back muscles, reducing fatigue and serving as a reminder to use correct methods (NIOSH, 1994). Back belts should be seen as an adjunct to proper lifting practices, not a primary means of prevention.
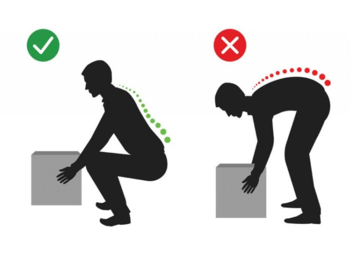
Correct Lifting Techniques
To lift safely, keep your knees bent to flatten your back and relieve muscle fatigue. When working at low levels, bend your knees deeply to avoid back strain. Ensure your footing is secure and firm before lifting. Dismount ladders and equipment slowly, lowering yourself with your hands, and never jump off (OSHA, 2016a).
When climbing onto equipment or ladders, secure your footing. Move ladders instead of reaching to prevent overextension. Avoid climbing on tables or chairs to reach high objects. Use tools like hoists, lifts, and dollies to save work and prevent strain, ensuring they are not overloaded (OSHA, 2016b).
Proper Posture and Ergonomics
While shoveling or using a rake, stand close to your work and keep your hands widely separated for leverage. Lift with your knees and keep your back straight, avoiding twisting motions. When driving, keep your seat forward with knees bent higher than your hips, and change positions frequently to prevent stiffness (OSHA, 2016b).
Exercise and Preparation
Warm-up exercises are crucial in preparing for physical tasks, similar to how athletes prepare before competitions. Simple exercises can loosen the back and help prevent injuries (NIOSH, 1994). Regular physical activity maintains flexibility and strength, contributing to overall back health.
Conclusion
Proper lifting techniques, combined with the use of back belts and ergonomic practices, are essential in preventing back injuries. Following guidelines from OSHA, NIOSH, and ACP can help maintain back health in occupational settings. Regular exercises and proper preparation further enhance safety and reduce the risk of injury.
References
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. (1994). Back belts: Do they prevent injury? Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/94-127/
Occupational Safety and Health Administration. (2016a). OSHA 29 CFR 1926: Safety and Health Regulations for Construction. Retrieved from https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/regulations/standardnumber/1926
Occupational Safety and Health Administration. (2016b). OSHA 29 CFR 1910: Occupational Safety and Health Standards. Retrieved from https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/regulations/standardnumber/1910
American College of Physicians. (2021). Clinical guidelines on back pain. Retrieved from https://www.acponline.org/clinical-information/guidelines
Detailed Analysis and Recommendations
To ensure the effectiveness of these practices, it is important to integrate them into daily routines and workplace safety protocols. Regular training sessions and workshops should be conducted to reinforce proper lifting techniques and the use of ergonomic tools. Employers must provide access to appropriate lifting equipment and ensure that employees are aware of how to use it correctly.
Implementation of Safety Programs
Developing and implementing comprehensive safety programs is crucial. These programs should include:
- Training on Proper Lifting Techniques: Regularly scheduled training sessions should focus on teaching employees the correct methods for lifting various weights and types of materials.
- Use of Back Belts: While not a substitute for proper technique, back belts can provide additional support. Training should include instructions on when and how to use back belts effectively.
- Ergonomic Assessments: Regular assessments of workstations and tasks can help identify potential hazards and areas for improvement. Adjustments should be made to minimize the risk of injury.
- Exercise Programs: Encouraging regular exercise can help maintain overall physical health and flexibility. Simple stretches and warm-up exercises should be incorporated into daily routines.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Continuous monitoring and evaluation of safety programs are essential. Feedback from employees should be collected to assess the effectiveness of the training and any implemented changes. Regular audits and inspections can help ensure compliance with safety standards and identify new hazards.
Conclusion
By adhering to the outlined guidelines and incorporating them into a comprehensive safety program, workplaces can significantly reduce the risk of back injuries. This proactive approach not only ensures the well-being of employees but also enhances productivity and reduces downtime caused by injuries.
References
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. (1994). Back belts: Do they prevent injury? Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/94-127/
Occupational Safety and Health Administration. (2016a). OSHA 29 CFR 1926: Safety and Health Regulations for Construction. Retrieved from https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/regulations/standardnumber/1926
Occupational Safety and Health Administration. (2016b). OSHA 29 CFR 1910: Occupational Safety and Health Standards. Retrieved from https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/regulations/standardnumber/1910
American College of Physicians. (2021). Clinical guidelines on back pain. Retrieved from https://www.acponline.org/clinical-information/guidelines


